LED Strips: Installing, repairing, and replacing them safely

Quick access links: Click on any link to jump to the section most relevant to you
Purpose of this article
In our previous FAQ about LED lighting, we cover a large number of questions related to the technical factors behind LED technology, and the installation of LED lighting systems. In this new article, we answer many questions received from homeowners in San Antonio about LED strips, how they work and don’t work, how to choose them, how to install them, what are the risks associated with them, etc.
This page with grow over time, as we get more questions from our San Antonio customers and we run into even more specific installation issues. If you have questions not answered here, please feel free to use the contact form on our site to ask us for answers. You can also communicate with us directly on our Facebook page.
Our experience
All Star Electric San Antonio installs all types of LED lighting systems in homes, offices, and retail spaces, and these systems often include LED strips. We know the technology and its requirements very well. If you think of installing an LED lighting system, don’t hesitate to call us at (210) 391-0274 to ask for a technical evaluation and an estimate.
Important: why LEDs are low-voltage and therefore less dangerous to handle than standard electrical bulbs, it does not mean they are without any danger. As always, we recommend non-professionals to call a professional electrician like All Star Electric to install, repair, inspect, and replace any electrical system. We only publish this information on our website for informational purpose, and not as a step-by-step guide to installing any electrical system.
CUTTING LED STRIPS

Can you just cut LED strips?
Only cut the strips at the designated cut points to ensure they function correctly. One of the most common errors we see homeowners doing when they install these strips, is to cut them in the wrong areas of the strip, damaging the circuitry. Once damaged, the strip becomes unusable.
Where is the best place to cut LED strips?
The only place to cut your strips is at the designated cut points, between 2 copper dots. The cut points are marked with a line or scissor icon. In low quality strips, this mark may be missing. Also, when you purchase strips, look on the package if they are cuttable. It will be indicated. If not, don’t buy them.
Where do you cut strips with no cut line?
That’s the issue with low-quality LED strips that don’t have designated cut lines: you don’t know where to cut them. Call a professional electrician like All Star Electric San Antonio or ask an employee of the store where you bought the strips to help you. Don’t cut without knowing where to.
How many times can you cut LED light strips?
It depends on the number of cut points available on the strip. Typically, you will find cut lines every inch or two. The more LED per unit of length, the smaller you can cut the strips.
The longer the distance between 2 cut lines, the more likely your LED strip will show uneven lighting (dark, bright, dark, bright, etc.).
If you want to be able to cut to the right length every time for your application, buy strips with more LEDs per unit of length.
Can you use the rest of a LED strip after cutting it?
Yes, you can use the remaining part of the LED strip after cutting it, provided you have the necessary connectors and power supply to operate it (and also provided you didn’t cut it at the wrong place).
Here is a useful video showing how to cut and reconnect LED strip lights
What are different types of connectors and power supply units for LED strips?
Power Supply (or LED Driver):
The LED driver converts the AC voltage of the mains to the DC voltage suitable for the LED strip. The power supply voltage rating (e.g., 12V or 24V) must match the voltage rating of the strip. Typically, LED strips are sold with their power supply so you don’t have to worry about it. However, if you cut a strip in multiple segments, then you have to either use connectors to reconnect to a powered strip or use a new power supply to feed voltage to the segment. Read what’s written on the strip to buy the right power supply.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The rating in amps or watts of the power supply must be able to handle the total current draw or power consumption of the strip. The longer the strip, the more LEDs on it, the more power it will consume. To pick the right power supply for your LED strip, multiply the total draw (in Watts) of the strip by 1.2x. This gives you a bit of safety margin.
LED strip connectors:

Strip-to-strip connectors – You use them to join two strands of strip together. They come as “clip-ons” (no soldering) or require soldering.
Strip-to-power connectors – Use these to connect the strip to the power supply. They typically have a clip or screw terminal on one end for the LED strip, and a barrel jack or wire leads on the other end for the power supply.
L-shape, T-shape, or Cross-connectors – These are used for creating corners or branching paths with strips. Useful if you want a light up a shelf over and/or under for instance, and you start the strip alongside a wall before branching out to the shelf.
What is a controller for RGB or smart LED strips?
A controller enables you to change the color, brightness, or pattern of RGB (Red-Green-Blue) LED strips. It can be a simple handheld remote unit or a wall-mounted unit. You can also pair smart strips with a dedicated smartphone app.
Some controllers also come with integrated power jacks, eliminating the need for a separate strip-to-power connector.
Can you add a dimmer to an LED strip?
Yes, as long as it is LED-compatible. it must be installed between the power supply and the strip. Dimmers are a practical way to create layers of lighting intensity in a room and to give more depth to your living space.
What are end caps for LED strips?
End-caps are small terminations that seal the cut ends of waterproof LED strips to maintain their IP rating (IP 65, 67, 68).

Do LED strips come with mounting clips or brackets?
Not often. But you can buy them separately. They help secure the strip in place. Use clips if the adhesive backing on the strip isn’t sticking to the supporting surface (e.g., texture issue), or if you need to add a bit of space between the supporting surface and the strip to help with heat dissipation (in tightly packed areas, for instance).
What happens if you cut a strip in the middle?
If you cut an LED strip anywhere else than on the designated cut points, you will damage the circuitry and prevent that section of the strip from working.
If you risk damaging your strip or cut at the wrong place and create a fire hazard, it is safer and probably also cheaper to get a professional electrician like All Star Electric to install your strips and LED lighting system.
Can you cut L.E.D. string lights to make them shorter?
The keyword here is “string lights”. Not strip lights. Unlike strips, most string lights aren’t designed to be cut. Cutting them can damage their circuitry and render them unusable.
POWERING LED STRIPS
Can you feed power to a LED strip from both ends?
Yes, feeding power from both ends can help maintain consistent brightness across long strips, especially if there is a noticeable voltage drop towards the end of a strip. As electrical current travels through the conductive material of the LED strip, it encounters resistance. This resistance decreases the light intensity of the strip.
Why are my LED strips not as bright at the end?

This is due to a voltage drop, a common phenomenon in longer LED strips. To counteract this, you can feed power from both ends or use a higher voltage power supply and regulate it at intervals.
By “regulation”, we refer to the practice of using voltage regulators or converters at specific points along a long LED strip to maintain consistent voltage and brightness.
This technique is especially useful for “hardscaping” LED lighting installations, where LED strips can be very long. Hardscaping is designed to highlight certain features of your home or outdoor space (e.g., along a soffit or roof line, around a pool, or along a stairwell).
How does All Star Electric San Antonio regulate the supply of power at intervals along an LED strip?
We do this in a 5-step process when we set up or repair a LED lighting installation.
1. Assessment:
We measure the voltage at different points along the LED strip. If we observe a significant drop towards the end, we advise regulating the power at intervals.
2. Choosing the voltage regulator:
For LED strips, we typically use a “buck converter” or “step-down converter.” This device takes a higher input voltage and “steps it down” to a lower, consistent output voltage.
Then, we need to ensure the regulator output voltage matches the requirement for the strip (12V or 24V) and handles the current draw of the strip section it will power.
3. Installation points:
We determine where to place the regulators along the strip, e.g., at the midpoint of a very long strip or at multiple points for exceptionally long installations.
4. Installing regulators:
Then we cut the LED strip at the chosen points. We connect the input side of the regulator to the power supply, or the earlier section of the LED strip. Then we connect the output side of the regulator to the next section of the strip.
Eventually, we secure all connections by soldering or using clip-on connectors.
5. Powering up and testing:
Once everything is connected, we power up the LED strip. The brightness should now be more consistent across its length.
Note: In our experience, installing long LED strip is a job better left to a licensed electrician like All Star Electric San Antonio. Not to toot our horn uselessly, but we have seen our fair share of bad LED lighting installations, just because the homeowners did not have the instruments necessary to do the job, or because they just did not know enough about electricity to carry out the task in the first place. We appreciate the spirit of DIY, but some tasks are difficult to carry out and you risk facing disappointment and waste your time and resources if you don’t do them properly.
Can a strip be powered from the middle?
Indeed, LED strips can be powered from the middle, especially to maintain consistent brightness across a long strip.
Can I connect 2 strips to one power source?
Yes, two or more strips can be connected to a single power source, but the power supply must be able to handle the combined current draw of all connected strips.
The current draw is the amount of electrical current that a device (in this case, a strip) consumes when it is in operation. It is measured in amperes (A) or milliamperes (mA).
What is the typical current draw range for an LED strip?
The current draw of a strip varies based on several factors:
- Type of LED: Different LEDs, like SMD 3528, SMD 5050, or SMD 2835, have different current requirements.
- Density: The number of LEDs per meter or foot. A strip with more LEDs per meter will draw more current.
- Color: Different colors can have different current requirements. For instance, white or blue LEDs might draw more current than red or green LEDs.
- Brightness: Some strips are adjustable. More brightness = more current.
Typically, for common strips like the SMD 5050, the current draw might be around 20mA per LED. So, if you have a strip with 60 LEDs per meter, it would draw around 1.2A per meter (60 LEDs x 20mA = 1200mA = 1.2A).
How to determine the current draw of a L.E.D. strip?
To determine the current draw of a strip:
- Check the packaging or product label: Most of the times, the manufacturer will provide specifications on the packaging or directly on the reel of the strip. Look for a current rating in amperes (A) or milliamperes (mA).
- Refer to the product manual: If the strip came with a manual, it might contain detailed specifications, including the current draw.
- Visit the manufacturer’s website: If you know the brand or model of the strip, the manufacturer’s website might have detailed specifications. Sometimes, distributors do a better job at publishing relevant information than the manufacturers themselves. No disrespect meant, but the local distributors (wholesalers) of Chinese manufacturers usually do a more thorough job at providing the technical specifications of an electrical product because Customs and certification agencies require them.
- Measure with a multimeter: If you have a multimeter, you can measure the current draw directly. Set the multimeter to measure current (in the appropriate range), interrupt the positive power lead to the strip, and connect the multimeter in series. Ensure the LED strip is fully powered on during this test.
Why should you check the current draw of the L.E.D. strip when you buy it?
For several reasons:
- Power supply selection: Your power supply must be able to provide the total current required by your strip. If you are connecting multiple strips, add up the current draw of each strip and select a power supply that handles the combined total after you multiply it by 1.2x for safety.
- Safety: Overloading a power supply can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Performance: If your LED strip receives the correct current, it will emit an optimal brightness and will last longer.
This useful video describes in more details how to calculate the power you need for an LED strip.
How many volts can LED strips handle?
The voltage an LED strip can handle depends on its design. Common voltages are 5V, 12V, and 24V.
What is the voltage range of an LED strip?
The voltage range of an LED strip depends on its design. Common voltages include 5V, 12V, and 24V. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications.
What is an “LED driver” in the context of LED strips?
An LED driver is a device that regulates the power to an LED or a string of LEDs. It ensures that the LED receives the correct voltage and current for optimal performance.
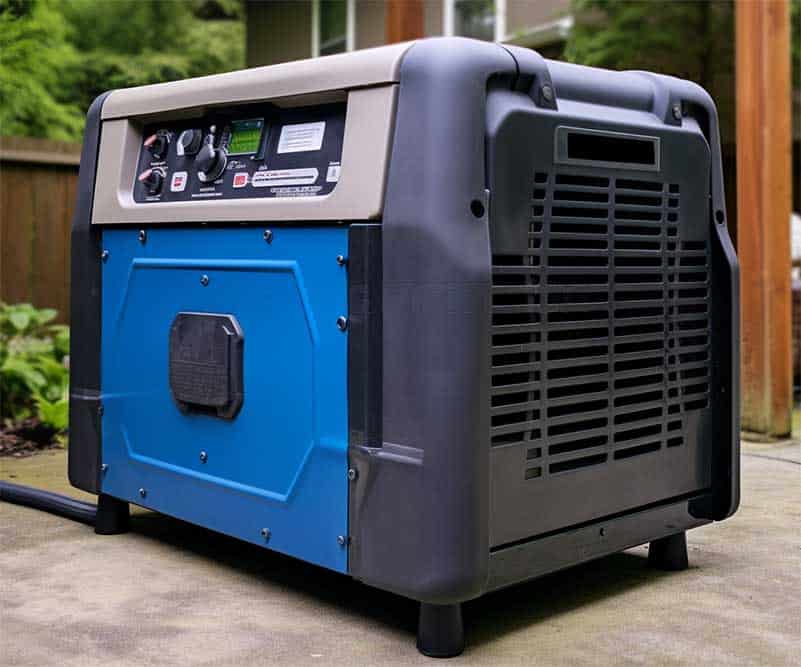
Can you power a LED strip with a battery?

Yes, batteries can power LED strips. The image on the left shows an example of a LED strip powered by a battery.

Why are there 3 pins on the plug of an LED strip?
The three pins typically correspond to the positive, negative, and data or control signal for RGB LED strips. Single-color strips don’t use the third pin.
Do LED strips need resistors and why?
Yes, LED strips often have resistors to regulate the current flowing through each LED, ensuring consistent brightness and preventing damage from excessive current.
Do all LED strips use the same amount of power per unit of time? Why?
No, the power consumption of LED strips varies based on factors like the type of LED, the number of LEDs per meter, and the voltage and current ratings of the strip. Additionally, the color(s) of a strip will impact its power usage.
Which colors in LED strip consume the most and the least power?
The power consumption of an LED varies according (in part) to its color.

RGB LED strips:
The power consumption of strips that combine red, green, and blue LEDs to produce various colors can vary according to the color being displayed. For example, displaying pure blue or white (all LEDs on) will typically consume more power than displaying pure red.
Typical current draw by color:
Red LEDs: These often have the lowest forward voltage, typically around 1.8 to 2.2 volts. As a result, they might consume less power than other colors when driven at the same current.
Green LEDs: These usually have a forward voltage in the range of 2.8 to 3.4 volts.
Blue and White LEDs: Both blue and white LEDs (white LEDs are often blue LEDs with a phosphor coating) typically have the highest forward voltage, often between 3.0 to 3.4 volts. Consequently, they might draw more power than red or green LEDs under the same conditions.
Different materials and bandgaps impact power consumption:
LEDs produce light by passing current through a semiconductor material. Different materials have different bandgaps, which determine the color (wavelength) of the emitted light. These materials can have varying levels of efficiency and voltage requirements.
Brightness vs. power consumption:
While the forward voltage is a factor, the perceived brightness is another consideration. To achieve a balanced brightness across different colors, some LEDs might be driven at a higher current, increasing their power consumption. For instance, a blue LED might be inherently brighter than a red one at the same current, so the red might be driven harder to match brightness levels, affecting its power consumption.
Practical implications:
When planning an LED installation, especially if you are concerned by power consumption, consider the colors that will be displayed most frequently. For instance, if you use an RGB strip that displays mostly white light (all 3 colors “on”), the power consumption will be higher than if you display just one color.
Which colors in LED strip use the least amount of power?
Generally, red LEDs consume less power compared to green or blue LEDs. However, actual power consumption can vary based on the design and manufacturer.
Will a 12V LED strip run on 9V?
A 12V LED strip might operate at 9V, but it will be dimmer than its intended brightness. Some strips might not light up at all if the voltage is too low.
CONNECTING LED STRIPS
Can I join two or more LED strips together?
Yes, LED strips can be joined using clip-on connectors or by soldering, depending on the type of strip and your expertise.
How many LED strips can you connect together?
The number of LED strips you can connect together depends on the capacity of the power supply and the total current draw of the combined strips. Always ensure the total current draw doesn’t exceed the rating of the power supply.

What to do with the ends of a LED strip?
The end of an LED strip can be sealed with endcaps to prevent dust and moisture ingress. If you plan to re-use the cut end, you can attach a connector for future extensions. Choose an IP67 rating for good waterproofing.
USING LED STRIPS SAFELY

Can LED strips be a fire hazard?
LED strips are much cooler than incandescent bulbs. But overheating occurs with poor quality LEDs and incorrect power supplies. Improper installations can create potential fire hazards. The quality of the product and the quality of workmanship at installation impact the safety of your system.
Is it safe to install LED strips under a bed?
Yes, it is safe to install LED strips under a bed for ambient lighting, provided that the installation is done correctly and the strips don’t overheat.
Is it safe to touch a LED strip?
Yes, LED strips are safe to touch when powered on, as they don’t generate a lot of heat. However, avoid touching any exposed wiring or connectors. These components heat up (even if slightly) and the heat needs to dissipate.
Is LED lighting explosion-proof?
LED fixtures rated as explosion-proof fall under Classifications C1D1 and C1D2. They also show an IP rating of at least IP54. These LED fixtures to be explosion-proof for use in hazardous environments. These fixtures have robust casings and are certified for such use. They are a bit of an “overkill” in a home environment.
How is Explosion-Proof protection rating calculated (e.g. IP54)?
Explosion-proof protection refers to the design of electrical equipment for use in hazardous areas where flammable gases or vapors may be present. The IP (ingress protection) rating, like IP54, indicates the level of protection against dust and water. The first digit (5 in IP54) refers to protection against solids, and the second digit (4 in IP54) refers to protection against liquids.
IP Ratings and Classifications are established by specific agencies:
Underwriters Laboratories (UL): One of the most recognized certification agencies in the U.S., UL tests and certifies products for safety. Products that meet their standards will carry the “UL Listed” mark.
Factory Mutual (FM) Global: FM is another major certification body that tests and certifies explosion-proof equipment for use in hazardous locations.
Intertek (ETL): Intertek’s ETL mark is another safety certification in the U.S. It indicates that the product has received testing procedures and meets the necessary safety standards.
Designations Applied to Explosion-Proof Certified LEDs:
Class: Defines the general nature of hazardous material in the surrounding atmosphere.
- Class I: Locations where flammable gases or vapors may be present.
- Class II: Locations where combustible dust may be present.
- Class III: Locations where ignitable fibers or flyings are present.
Division: Indicates the likelihood of the hazardous material being present in an ignitable concentration.
- Division 1: Hazardous materials are present under regular operating conditions.
- Division 2: Hazardous materials are present only under abnormal conditions, such as a container failure.
Group: Specifies the type of hazardous material in the surrounding atmosphere.
- Group A: Acetylene
- Group B: Hydrogen
- Group C: Ethylene
- Group D: Propane
- Group E: Metal dust (e.g., aluminum, magnesium)
- Group F: Coal dust
- Group G: Grain dust
Temperature Class (T-Code): Indicates the maximum surface temperature that a piece of equipment can reach. It ensures that the equipment won’t ignite the specific gas or vapor. For example:
- T1: 450°C
- T2: 300°C
- T3: 200°C
- T4: 135°C
- T5: 100°C
- T6: 85°C
When looking at explosion-proof LED fixtures or equipment, you will see labels like “Class I, Division 1, Groups C and D, T4”. This would indicate that the LED is suitable for locations with flammable gases or vapors (Class I) that are regularly present (Division 1), specifically ethylene and propane (Groups C and D), and that the maximum surface temperature of the LED is 135°C (T4).
What happens if you put too much power into an LED?
Overpowering an LED causes it to overheat. This reduces its lifespan and cause it to burn out. All Star Electric San Antonio always use the power supply recommended by the manufacturer.
What happens when a LED gets too hot?
Excessive heat degrades LED performance and reduces its lifespan. LED longevity partly depends on normal heat dissipation.
What is Class 1 Div 1 LED Lighting (C1D1)?
Class 1 Div 1 (C1D1) LED lighting can serve in areas where flammable gases or vapors are continuously or frequently present under normal operating conditions. These lights meet strict safety standards for such environments.
Can you define Electrical Overstress (EOS) in the context of LED strips?
Electrical Overstress (EOS) refers to the condition where an LED strip receives a voltage or current beyond its maximum rated limits. This damage the LED and reduces its lifespan.
Can you define Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) in the context of LED strips?
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) refers to the sudden flow of electricity between two charged objects. In the context of LED strips, ESD damages LEDs if handled without proper precautions.
What is Reverse Bias in the context of LED strips?
Reverse bias occurs when voltage applies in the opposite direction of the normal operation of the LED. LEDs can handle a small reverse voltage, but excessive reverse bias will damage them.
What do the acronyms IP54, IP55, IP65 mean in the context of LEDs and LED strips?
IP ratings indicate the level of protection an electrical device has against solids and liquids. In IP54, for example, the ‘5’ indicates protection against limited dust ingress, and the ‘4’ indicates protection against water splashes. Similarly, IP55 offers protection against limited dust ingress and low-pressure water jets, while IP65 is dust-tight and protected against water jets.
This is an excellent resource for IP ratings explanations.
Is it safe to install LED strips outside as Christmas decorations? Why?
Yes, it is safe to use LED strips as outdoor Christmas decorations, provided their rating is for outdoor use (e.g., they must have a suitable IP rating – See IP rating explanation in this FAQ, and check the IP rating table on this site). Strips rated for outdoor can withstand moisture and temperature variations.
Which types of LED strips will run the hottest?
High-density LED strips with more LEDs per meter and high-power LEDs tend to run hotter than other types. These strips must be installed so that heat dissipation happens. It is not advisable to install them in confined, non-ventilated spaces. Consult with a licensed electrician like All Star Electrical San Antonio.

Can you safely install LED strips in an attic where blown-in insulation material is present?
LED strips produce less heat than traditional bulbs BUT they MUST receive proper ventilation and can’t be covered by insulation which can trap heat. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation recommendations. Consult with San Antonio licensed electrician All Star Electrical to understand the requirements and the risks. Call us at (210) 391-0274.
What if you plug an LED strip into the AC mains?
Plugging an LED strip directly into AC mains without an appropriate driver or transformer will damage the strip because most LED strips operate on low-voltage DC.
TROUBLESHOOTING LED STRIPS
What causes LED strips to stop working?
There are various reasons to LED stopping to work: damaged LEDs, broken circuitry, power supply issues, faulty connectors…
What causes LED lights to explode?
While rare, LED lights can “explode” or burst due to manufacturing defects, overheating, power surges, or using incorrect power supplies.
What causes LED strip lights to flash?
LED strip lights can flash due to power supply issues, faulty LEDs, or incompatible dimmer switches.
Dimming LED strips is more complex than dimming traditional incandescent bulbs due to the differences in their electrical characteristics.

What properties does a dimmer switch need to have to be compatible with an LED strip?
These are the most common type of dimmers used for incandescent and halogen bulbs. They work by cutting off part of the voltage waveform, either on the leading edge or trailing edge. While some LED drivers are designed to be compatible with phase-cut dimmers, not all are.
- Leading edge (Triac) dimmers: These are traditional dimmers primarily designed for incandescent lamps. They might not be compatible with many LED drivers.
- Trailing edge (ELV) dimmers: These are more modern and are often more compatible with LED drivers.
Why can LED dimmers produce EMI?
Some poorly designed dimmers can produce EMI (electro-magnetic interference), which can interfere with other electronic devices. Good quality dimmers have filtering to minimize EMI.
Check the dimmer’s packaging or product data sheet. It should indicate if it is LED compatible. Some might even list specific tested LED brands or models.
Sometimes, the best way to determine compatibility is through testing. Install the dimmer and observe how your LED strip perform. Look for issues like flickering, limited dimming range, or buzzing sounds.
CHOOSING LED STRIP COLORS
Why is blue the “most difficult LED color”?
Blue LEDs require a higher voltage to operate. Their composition includes more complex semiconductor materials than red or green LEDs. Blue LEDs also tend to have a shorter lifespan and are more sensitive to temperature variations.
Which are the 3 brightest LED strip colors?
The perceived brightness can vary, but research generally rates white, blue, and green the brightest LED strip colors.
How do you accurately measure the brightness of an LED strip?
We measure the brightness of an LED strip in lumens. Use a light meter or lux meter to measure the luminous flux or brightness of an LED strip.
Can LED strips favor a deeper, more relaxing sleep? If so, which colors and what color range (in Kelvin)?
Warm-colored LED strips, especially those in the red to orange spectrum (around 2000K to 3000K), can promote relaxation and potentially aid sleep. Blue light, on the other hand, can suppress melatonin production and disrupt sleep.

What are the differences between an LED strip and LED string lights?
Both LED strips and LED string lights have distinct characteristics and are typically used for different purposes. We break it down under 6 characteristics: • Physical structure • Purpose & Application • Power & control • Flexibility & installation • Durability & waterproofing • Appearance.
1. Physical structure:
- LED strips:
- These are flexible circuit boards with LEDs mounted on them at regular intervals.
- They often come with adhesive backing for easy installation.
- They are typically flat and can be cut at specific intervals (cut points) to fit various lengths.
- LED string lights:
- LED string lights consist of individual LED bulbs connected by wires or strings, housed in plastic or glass.
- They come with hooks or clips for easy installation.
- Unlike LED strips, they cannot be cut at specific intervals and are commonly used for decorative lighting indoors and outdoors.
2. Purpose & Application:
- LED strips:
- Commonly used for accent lighting, under-cabinet lighting, backlighting, and other decorative purposes.
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor use, depending on their waterproof rating.
- Can be used in architectural applications for cove lighting or highlighting features.
- LED string lights:
- Often used for decorative lighting, including for events, holidays, and ambiance creation.
- Versatile for indoor and outdoor use, depending on their weatherproof rating.
- Can be used to create linear lighting effects and highlight decorative and architectural features.
3. Power & control:
- LED strips:
- Typically powered by a direct current (DC) source, requiring a power adapter or driver to convert from the mains AC voltage.
- Can be dimmable and, in the case of RGB strips, color-changing with the use of controllers.
- LED string lights:
- Commonly powered by a direct current (DC) source, often requiring a power adapter for conversion from mains AC voltage.
- Can have dimmable options and, in the case of RGB string lights, color-changing capabilities facilitated by controllers.
4. Flexibility & installation:
- LED strips:
- Highly flexible and can be bent around corners or curved surfaces.
- Often come with adhesive backing for easy installation on flat surfaces.
- LED string lights:
5. Durability & waterproofing:
- LED strips:
- Available in various waterproof ratings, from IP20 (not waterproof) to IP68 (fully submersible).
- Encased in silicone or epoxy for protection in waterproof versions.
- LED string lights:
- Less flexible than LED strips and typically designed for linear installations.
- May have some degree of flexibility but are generally less adaptable to curved or irregular surfaces.
- Commonly come with hooks, clips, or other attachment mechanisms for straightforward installation on various surfaces.
6. Appearance:
- LED strips:
- Provide a continuous, linear light source.
- LEDs are closely spaced, offering a more uniform light output.
- LED string lights:
- Provide a dispersed light source with individual bulbs spaced along a linear arrangement.
- Their appearance is characterized by distinct points of light, creating a decorative and festive ambiance.
- Unlike LED strips, the spacing between bulbs results in a less uniform light output.
Here is a very good video giving sound advice on how to choose good quality LED light strips, and the driver to power them up.
More questions coming soon…
About All Star Electric San Antonio
As professional electricians in San Antonio, All Star Electric San Antonio installs, repairs, and inspects all types of electrical systems, both in home, offices and retail spaces. With the advent of LED technologies, lighting systems can now “sculpt” the atmosphere of a home indoors and outdoors. In office and retail setting, LEDs increase productivity, serve to highlight products, and render color more truthfully than incandescent bulbs and neon lights.
All Star Electric San Antonio is also a Certified Tesla installer of Level 1 and Level 2 charging systems for EVs.
We have been in business in San Antonio almost 30 years, and we serve the whole San Antonio community and neighboring cities such as Helotes, Selma, Castle Hills and Alamo Heights. We keep an A+ rating at the BBB San Antonio.
Additional Resources
LED Lighting: one of our specialties
Installing dimmer switches